All Blogs

Sleep Deprivation: Causes, Symptoms, and Serious Health Effects
Sleep deprivation is a widespread health concern that occurs when individuals consistently fail to receive adequate, restorative sleep. In today’s fast-paced lifestyle, people often ignore sleep needs, prioritizing work, screens, and social responsibilities instead. As a result, sleep deprivation gradually affects physical strength, emotional balance, cognitive performance, and long-term hea [...]

Winter Cough in Children: Causes, Types, and Effective Care Tips
The winter season brings joy and chilly winds, but it also brings a winter cough in children, which many parents worry about each year. This common problem affects kids because colder weather increases the spread of viruses and stresses young immune systems that are still developing. Understanding the causes, types, and ways to care for your child helps you manage coughs confidently and reduce com [...]
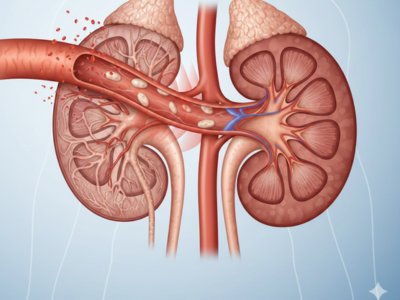
How High Blood Pressure Silently Destroys Your Kidneys
High blood pressure, medically known as hypertension, is a powerful and silent threat to your kidneys that quietly causes damage long before symptoms appear. In fact, persistently elevated blood pressure levels gradually weaken and injure delicate blood vessels, making the kidneys less able to filter blood efficiently and maintain fluid balance. This unseen harm often continues for years, and only [...]
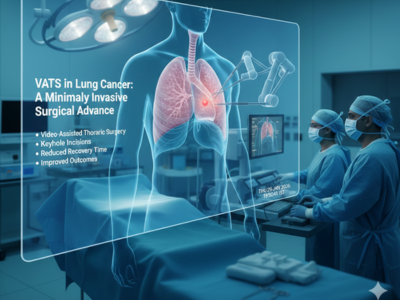
VATS in Lung Cancer: A Minimally Invasive Surgical Advance
VATS in lung cancer represents a significant advancement in thoracic surgery, offering minimally invasive solutions for diagnosis and treatment. This technique allows surgeons to access the chest cavity using small incisions, specialized instruments, and a high-resolution camera. Consequently, patients experience reduced trauma, faster recovery, and improved postoperative comfort compared to tradi [...]
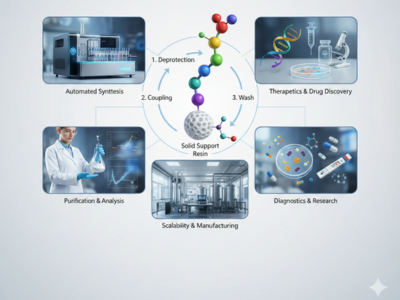
Peptide Synthesis: A Complete Guide to Modern SPPS Advantages
Peptide synthesis plays a critical role in modern pharmaceutical development, biotechnology research, and diagnostic innovation worldwide. Scientists rely on Peptide synthesis to construct short amino acid chains that replicate biological functions with high precision. Consequently, this capability supports drug discovery, therapeutic development, and advanced biomedical research. Among available [...]
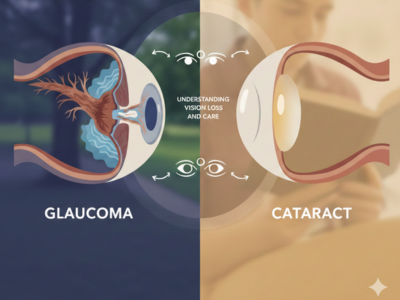
Glaucoma vs Cataract: Understanding Vision Loss and Care
Understanding Glaucoma vs Cataract is essential for protecting vision and maintaining long-term eye health at every stage of life. Both conditions remain leading causes of visual impairment worldwide; however, they affect the eyes in very different ways. Therefore, recognizing their differences helps individuals seek timely treatment and reduce the risk of permanent vision loss. Moreover, awarenes [...]
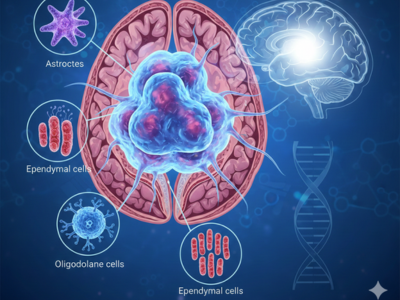
Glioma Brain Tumour: Types, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
A glioma brain tumour develops when glial cells in the central nervous system grow uncontrollably, forming a mass that can affect critical brain functions. These tumours originate from cells that normally support neurons, maintain the brain’s microenvironment, and ensure proper neurological activity. When these cells turn abnormal, they can interfere with cognitive, motor, and sensory functi [...]
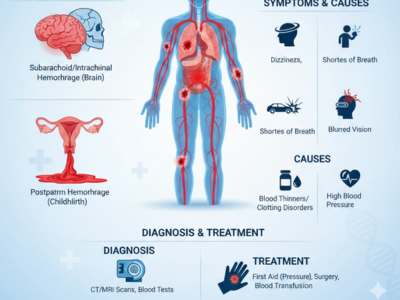
Hemorrhage: Types, Symptoms, Causes & Treatment Guide
Hemorrhage is a medical condition that involves significant blood loss from damaged blood vessels, and it can affect people of any age at any time. In fact, this kind of excessive bleeding can happen inside the body or outside, and when it goes unnoticed or untreated, it can lead to serious complications such as shock, organ failure, or even death. Therefore, understanding hemorrhage is crucial fo [...]
Radiation Therapy for Cancer: What to Expect at Every Stage
Radiation Therapy is a widely used cancer treatment that helps destroy cancer cells and control tumor growth effectively. It plays a crucial role either alone or combined with surgery and chemotherapy. Although Radiation Therapy targets cancer cells precisely, it can also affect nearby healthy tissues, which leads to side effects. Understanding what happens before, during, and after Radiation Ther [...]

ACV Benefits: Why This Humble Vinegar Now Runs the Show
For decades, apple cider vinegar (ACV) lived a quiet life. It resided mostly in kitchen pantries. Its primary role was dressing salads. Sometimes, it helped pickle vegetables. It was a culinary workhorse, dependable but unsung. However, this pantry staple is now having a serious moment. Today, ACV is a wellness superstar. It is a beauty industry darling. Furthermore, it is a formidable market play [...]